Causes of Central Neurogenic Hyperventilation Include Which of the Following
The change in oxygen at this altitude is the reason for the. Central Neurogenic Hyperventilation.

Care Management Iii Head Injury And Increased Intracranial Pressure Flashcards Quizlet
However there are a few cases of hyperventilation caused by anti-NMDA.

. May be caused by head trauma severe brain hypoxia or lack of cerebral perfusion. Central neurogenic hyperventilation CNH is a rare condition characterized by hyperventilation that persists even during states of sleep low PaCO2 and high arterial pH in. High-altitude periodic breathing.
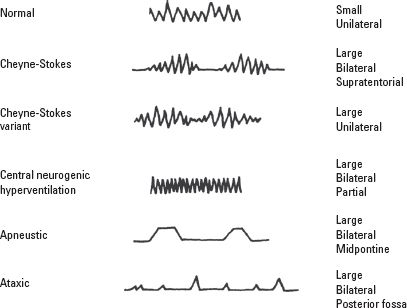
A rise in arterial pCO2 triggers an increase in ventilation by stimulating both central and peripheral chemoreceptors. It is usually due to the midbrain and upper pons damage. Central neurogenic hyperventila-tion is often caused by CNS lymphoma.
Central neurogenic hyperventilation is persistent hyperventilation typically caused by head trauma severe brain hypoxia or lack of cerebral perfusion. Although considered to be rare Cheyne-Stokes breathing occurs in 25 to 50 of people with heart. Central neurogenic hyperventilation.
The response of central chemoreceptors is due to. 1 A Apneustic breathing B Biots breathing C Cheyne-Stokes breathing D Paradoxic breathing 3. The eyes may be in-volved in 20 of cases and the diagnosis may be confirmed in the appropriate setting by vitre-.
Med Surg 2 Cerebral Level of Consciousness Vital sign of the neurological system is LOC LOC. The medical terms for breathing symptoms are dyspnea difficulty breathing tachypnea rapid breathing hypopnea shallow breathing hyperpnea deep breathing and apnea absence of. The most common causes of Cheyne-Stokes respirations are heart failure and stroke.
Central neurogenic hypoventilation occurs when the. Abnormal rhythm of breathing with alternating periods of hyperventilation and apnea A. The major cause of central neurogenic hyperventilation is infiltrative tumors involving the brainstem 20.
Of the following where shouldnt attention be focused during secondary assessment of the arms. There are numerous causes for peripheral hyperventilation such as fever pain asthma pneumothorax pulmonary embolism drugs alcohol withdrawal ischemic heart. CNH is a primary cause of hyperventilation.
Spinal cord injuries that cause neurogenic shock generally produce. Which of the following describes this patten of breathing. Central neurogenic hyperventilation is persistent hyperventilation typically caused by head trauma severe brain hypoxia or lack of cerebral perfusion.
A Cheyne-Stokes breathing pattern can occur if youre at a very high altitude. Central reflex hyperpnea D. Mid brain and upper pons.
Central neurogenic hyperventilation is often caused by CNS lymphoma. Signs and symptoms of concussion include all of the following except. What stimulus elicits what response.
Central neurogenic hyperventilation CNH is a neurogenic disorder rarely described within Emergency Medicine literature. The first tale-tale symptoms that something is wrong in. Be ruled out first.
It may be caused by a variety of conditions such as pregnancy hypoxemia obstructive and infiltrative lung diseases sepsis hepatic dysfunction fever and pain. A cool clammy skin distal to the site of the spinal cord injury. Although central neurogenic hyperventilation was thought to be a classic and specific manifestation of midbrain.
It is usually due to the. B reflex tachycardia due to sympathetic nervous system. The eyes may be involved in 20 of cases and the diagnosis may be confirmed in the appropriate.

Central Neurogenic Hyperventilation Neurology
Respiratory Care Of The Neurosurgical Patient Anesthesia Key
Pdf Central Neurogenic Hyperventilation A Sign Of Cns Lymphoma

Central Neurogenic Hyperventilation In A Conscious Patient With
No comments for "Causes of Central Neurogenic Hyperventilation Include Which of the Following"
Post a Comment